

- #Open vnc viewer command line install#
- #Open vnc viewer command line update#
- #Open vnc viewer command line password#
- #Open vnc viewer command line windows#
The commands that the VNC server runs at startup are located in a configuration file called xstartup in the. Specifically, VNC needs to know which graphical desktop environment it should connect to. The VNC server needs to know which commands to execute when it starts up. Now let’s configure it to launch Xfce and give us access to the server through a graphical interface.
#Open vnc viewer command line password#
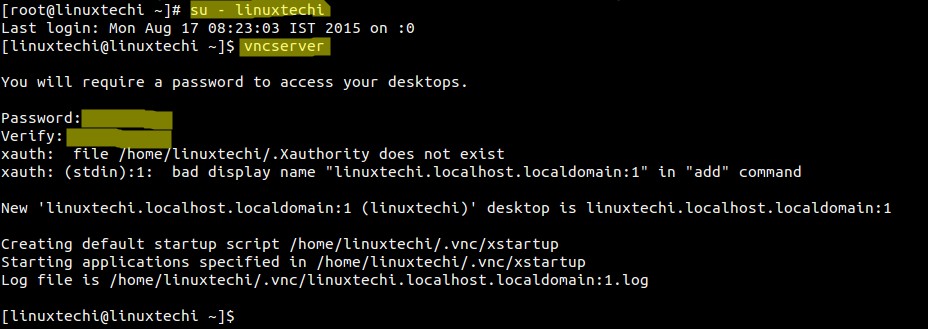
Note that if you ever want to change your password or add a view-only password, you can do so with the vncpasswd command:Īt this point, the VNC server is installed and running. Log file is /home/ sammy/.vnc/ your_hostname:1.log Starting applications specified in /home/ sammy/.vnc/xstartup Xauth: file /home/ sammy/.Xauthority does not existĬreating default startup script /home/ sammy/.vnc/xstartup OutputWould you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n You’ll be prompted to enter and verify a password to access your machine remotely: Next, run the vncserver command to set a VNC access password, create the initial configuration files, and start a VNC server instance:
#Open vnc viewer command line install#
Once that installation completes, install the TightVNC server: So for the purposes of this tutorial, your choice of display manager isn’t pertinent. You’ll only be using Xfce when you connect with a VNC client, and in these Xfce sessions you’ll already be logged in as your non-root Ubuntu user. A display manager is a program that allows you to select and log in to a desktop environment through a graphical interface. Now install Xfce along with the xfce4-goodies package, which contains a few enhancements for the desktop environment:ĭuring installation, you may be prompted to choose a default display manager for Xfce.
#Open vnc viewer command line update#
Both Xfce and TightVNC are known for being lightweight and fast, which will help ensure that the VNC connection will be smooth and stable even on slower internet connections.Īfter connecting to your server with SSH, update your list of packages: In this tutorial, you will install packages for the latest Xfce desktop environment and the TightVNC package available from the official Ubuntu repository. You have many options when it comes to which VNC server and desktop environment you choose. Step 1 - Installing the Desktop Environment and VNC Serverīy default, an Ubuntu 20.04 server does not come with a graphical desktop environment or a VNC server installed, so you’ll begin by installing those.
#Open vnc viewer command line windows#
Where vncterm in the above output is used by Linux VMs and qemu-dm by Windows VMs.ĭownload and configure your PuTTY SSH client ( ) with (multiple) tunnels as shown in the following screen shot: Using the Graphical User Interface In XenServer, all VNC connectors inside Dom0 listen on ports starting from 5900 (Dom0 itself), 5901 (first VM), and so on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
